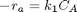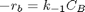Contents
Using cmu.units in Matlab for basic calculations
note you need to install the +cmu package for this to work.
clear all; clc; close all;
Load the units package
units is a new type of object in Matlab that stores the units, enforces proper unit algebra and works with most mathematical operations in Matlab. You load the units package into a variable; by convention: u the default set of base units are the SI units.
u = cmu.units;
Simple unit algebra
the basics of unit algebra are that like units can be added and subtracted. Unlike units can be multiplied and divided. when you assign a unit to a number, it is automatically converted into the base units.
5*u.kg
5*u.lb
6*u.m/u.s
1*u.m + 10*u.cm
5*kg
2.26796*kg
6*m/s
1.1*m
Temperature is a little special
most unit conversions are simple multiplications. Temperature conversions involve multiplication and an offset; e.g. F = C*9/5 + 32;
T = 298*u.K
Tf = 400*u.R
T1 = u.degC(100)
T2 = u.degF(212)
u.degF2C(32)
u.degC2F(100)
298*K
222.222*K
373.15*K
373.15*K
ans =
0
ans =
212
displaying units
a unit object has an "as" function that can display the unit in various forms
a = 1*u.kg;
a.as(u.lb)
sprintf('%1.2f = %1.2f lb',a,a/u.lb)
ans =
2.205*lb
ans =
1.00 kg = 2.20 lb
Load the cmu.constants package
The gas constant, speed of light, etc... are stored in this package
clear all; u = cmu.units;
c = cmu.constants;
c.R
c.R.as(u.J/u.mol/u.K)
c.R.as(u.J/(u.mol*u.K))
c.R.as(u.cal/u.mol/u.K)
c.R.as(u.dm^3*u.atm/u.mol/u.K)
c.R.as(u.BTU/u.lbmol/u.R)
c.R.as(u.ft^3*u.atm/(u.lbmol*u.R))
8.31447*m^2/s^2*kg/K/mol
ans =
8.314*J/mol/K
ans =
8.314*J/(mol*K)
ans =
1.986*cal/mol/K
ans =
0.082*dm^3*atm/mol/K
ans =
1.986*BTU/lbmol/R
ans =
0.730*ft^3*atm/(lbmol*R)
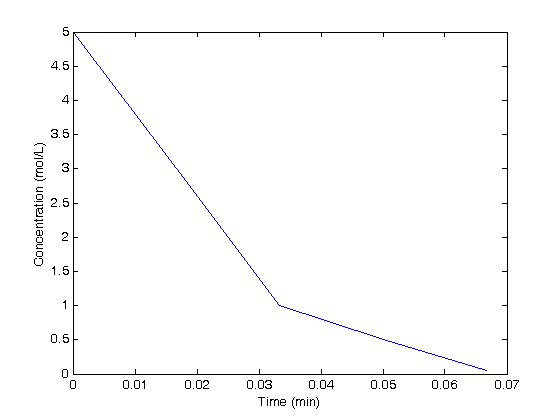
Arrays of units
t = [0 1 2 3 4]*u.s;
C = [5 3 1 0.5 0.05]*u.mol/u.L;
plot(t/u.min,C/(u.mol/u.L))
xlabel('Time (min)')
ylabel('Concentration (mol/L)')
units with Matlab functions
Many functions in Matlab such as ode45, ode15s, fzero, fsolve, min, max, etc... work with units. This works because we have overloaded these functions to work with units. Not all functions are overloaded though, so be careful! If you find you have lost the units, it means you used a function that was not overloaded. Please let us know about it!
functions that do not work with units
functions that require dimensionless arguments (e.g. trig functions, exp, log, etc...) will usually fail if you pass a unit in. You must divide the arguments by the appropriate units to make them dimensionless
a = 5*u.mol;
sin(a/u.mol)
ans =
-0.9589
Alternative base units
you can specify 'SI', 'CGS' or 'American' as the base units SI/MKS: {'m','s','kg', 'K', 'mol','coul'} CGS: {'cm','s','gm','K', 'mol','coul'} American: {'in','s','lb','R', 'mol','coul'
u = cmu.units('American');
a = 2*u.ft
a.as(u.m)
u = cmu.unit.units('mm','min','ton','R','coul','mol');
a = u.cm
a.as(u.m)
24*in
ans =
0.610*m
10*mm
ans =
0.010*m
simplified units
there may be times when you need units conversion, but you only want simple numbers and not unit objects, e.g. because some Matlab function doesn't handle units. You can load the simple_units structure to get a set of conversion factors. Unit algebra is not used and units are kept track of, so you have to know what the units are.
u = cmu.unit.simple_units;
a = 1*u.kg
a/u.lb
a/u.min
a =
0.0011
ans =
2.2046
ans =
0.0011
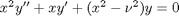 comes up often in engineering problems such as heat transfer. The solutions to this equation are the Bessel functions. To solve this equation numerically, we must convert it to a system of first order ODEs. This can be done by letting
comes up often in engineering problems such as heat transfer. The solutions to this equation are the Bessel functions. To solve this equation numerically, we must convert it to a system of first order ODEs. This can be done by letting 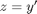 and
and 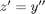 and performing the change of variables:
and performing the change of variables: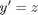
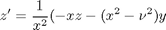
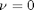 , the solution is known to be the Bessel function
, the solution is known to be the Bessel function 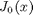 , which is represented in Matlab as besselj(0,x). The initial conditions for this problem are:
, which is represented in Matlab as besselj(0,x). The initial conditions for this problem are: 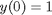 and
and 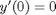 .
.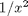 term, the ODEs are not defined at x=0.
term, the ODEs are not defined at x=0.
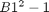 . We can read each cell. We can also write a value to B1, and then read B2 to get the value squared. finally, we will create a function that uses Excel to perform the calculation of squaring a number, and use fsolve to minimize the function.
. We can read each cell. We can also write a value to B1, and then read B2 to get the value squared. finally, we will create a function that uses Excel to perform the calculation of squaring a number, and use fsolve to minimize the function. . We try guesses above and below each one.
. We try guesses above and below each one.